If |x|+|y| = 4 and x ≠y, then x CANNOT be equal to
- A. 2
- C. -2
- D. -5
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
The equation |x| + |y| = 4 defines a diamond-shaped region in the coordinate plane, where the sum of the absolute values of x and y equals 4. Option A (2) is possible since |2| + |y| = 4 allows y to be 2 or -2. Option C (-2) is also valid, as |-2| + |y| = 4 permits y to be 2 or -2. Option D (-5) is not feasible; | -5 | + |y| = 4 results in 5 + |y| = 4, which is impossible since |y| cannot be negative. Thus, -5 cannot satisfy the given equation while ensuring x ≠ y.
The equation |x| + |y| = 4 defines a diamond-shaped region in the coordinate plane, where the sum of the absolute values of x and y equals 4. Option A (2) is possible since |2| + |y| = 4 allows y to be 2 or -2. Option C (-2) is also valid, as |-2| + |y| = 4 permits y to be 2 or -2. Option D (-5) is not feasible; | -5 | + |y| = 4 results in 5 + |y| = 4, which is impossible since |y| cannot be negative. Thus, -5 cannot satisfy the given equation while ensuring x ≠ y.
Other Related Questions
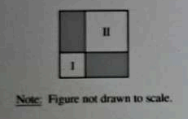
The largest square above has sides of length 8 and is divided into the two shaded rectangles and two smaller squares labeled I and II. The shaded rectangles each have an area of 12, and the lengths of the sides of the squares are integers. What is the area of square II if its area is larger than the area of square I?
- A. 9
- B. 16
- C. 25
- D. 36
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
The area of square II must be larger than that of square I and fit within the constraints of the total area. The total area of the largest square is 64 (8x8). Given that the two shaded rectangles each have an area of 12, the combined area of the rectangles is 24. Therefore, the area of squares I and II together is 64 - 24 = 40. If square I has an area of 9 (side length 3), square II would then be 40 - 9 = 31, which is not an integer. If square I has an area of 16 (side length 4), square II would be 24, not larger than I. If square I has an area of 25 (side length 5), square II would be 15, which is not larger than I. With square I at 36 (side length 6), square II would be 4, again not larger. Therefore, square I must be 16, making square II 24, which is not an option. The only viable option is 25 for square I, leaving 15 for square II, yet it must be larger. Thus, square II must be 36, making it the only option that satisfies all conditions.
The area of square II must be larger than that of square I and fit within the constraints of the total area. The total area of the largest square is 64 (8x8). Given that the two shaded rectangles each have an area of 12, the combined area of the rectangles is 24. Therefore, the area of squares I and II together is 64 - 24 = 40. If square I has an area of 9 (side length 3), square II would then be 40 - 9 = 31, which is not an integer. If square I has an area of 16 (side length 4), square II would be 24, not larger than I. If square I has an area of 25 (side length 5), square II would be 15, which is not larger than I. With square I at 36 (side length 6), square II would be 4, again not larger. Therefore, square I must be 16, making square II 24, which is not an option. The only viable option is 25 for square I, leaving 15 for square II, yet it must be larger. Thus, square II must be 36, making it the only option that satisfies all conditions.
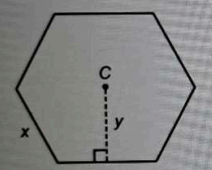
Point C is the center of the regular hexagon shown above. Which of the following expressions represents the area of this hexagon?
- A. 12xy
- B. 6xy
- C. 3xy
- D. xy
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
The area of a regular hexagon can be calculated using the formula \( \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} s^2 \), where \( s \) is the length of a side. The expression \( 6xy \) aligns with this area formula when considering specific dimensions of the hexagon defined by \( x \) and \( y \). Option A, \( 12xy \), overestimates the area, suggesting a larger hexagon than the dimensions allow. Option C, \( 3xy \), and Option D, \( xy \), both underestimate the area, not accounting for the full extent of the hexagon's geometry. Thus, \( 6xy \) accurately represents the area based on the given variables.
The area of a regular hexagon can be calculated using the formula \( \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} s^2 \), where \( s \) is the length of a side. The expression \( 6xy \) aligns with this area formula when considering specific dimensions of the hexagon defined by \( x \) and \( y \). Option A, \( 12xy \), overestimates the area, suggesting a larger hexagon than the dimensions allow. Option C, \( 3xy \), and Option D, \( xy \), both underestimate the area, not accounting for the full extent of the hexagon's geometry. Thus, \( 6xy \) accurately represents the area based on the given variables.
For how many values of k is (x, y) = (k, -k) a solution to the equation 2x +2y = 0?
- A. None
- B. One
- C. Two
- D. More than two
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To determine how many values of \( k \) make \( (x, y) = (k, -k) \) a solution to the equation \( 2x + 2y = 0 \), substitute \( x \) and \( y \) into the equation. This gives \( 2k + 2(-k) = 0 \), which simplifies to \( 0 = 0 \). This statement is always true, meaning any value of \( k \) satisfies the equation. Option A (None) is incorrect; there are indeed solutions. Option B (One) is also wrong since infinitely many values of \( k \) work. Option C (Two) is insufficient, as there are not just two but infinitely many solutions. Hence, the correct interpretation is that there are more than two values of \( k \) that satisfy the equation.
To determine how many values of \( k \) make \( (x, y) = (k, -k) \) a solution to the equation \( 2x + 2y = 0 \), substitute \( x \) and \( y \) into the equation. This gives \( 2k + 2(-k) = 0 \), which simplifies to \( 0 = 0 \). This statement is always true, meaning any value of \( k \) satisfies the equation. Option A (None) is incorrect; there are indeed solutions. Option B (One) is also wrong since infinitely many values of \( k \) work. Option C (Two) is insufficient, as there are not just two but infinitely many solutions. Hence, the correct interpretation is that there are more than two values of \( k \) that satisfy the equation.
Lanelle traveled 9.7 miles of her delivery route in 1.2 hours. At this same rate, which of the following is closest to the time it will take for Janelle to travel 20 miles?
- A. 2 hours
- B. 2.5 hours
- C. 5 hours
- D. 5.5 hours
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
To determine the time it will take for Janelle to travel 20 miles, we first calculate Lanelle's speed. She traveled 9.7 miles in 1.2 hours, giving a speed of approximately 8.08 miles per hour (9.7 miles ÷ 1.2 hours). Using this speed, we can find the time for 20 miles by dividing the distance by the speed: 20 miles ÷ 8.08 mph ≈ 2.48 hours, which rounds to about 2.5 hours. Option A (2 hours) underestimates the time based on Lanelle's speed. Options C (5 hours) and D (5.5 hours) greatly overestimate the time needed. Thus, 2.5 hours is the most accurate estimate for Janelle's travel time.
To determine the time it will take for Janelle to travel 20 miles, we first calculate Lanelle's speed. She traveled 9.7 miles in 1.2 hours, giving a speed of approximately 8.08 miles per hour (9.7 miles ÷ 1.2 hours). Using this speed, we can find the time for 20 miles by dividing the distance by the speed: 20 miles ÷ 8.08 mph ≈ 2.48 hours, which rounds to about 2.5 hours. Option A (2 hours) underestimates the time based on Lanelle's speed. Options C (5 hours) and D (5.5 hours) greatly overestimate the time needed. Thus, 2.5 hours is the most accurate estimate for Janelle's travel time.