Greatest?
- A. 245 thousandths
- B. 24 hundredths
- C. 3 tenths
- D. 2 fifths
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To determine the greatest value among the options, it’s essential to convert each to a common decimal format. A: 245 thousandths equals 0.245. B: 24 hundredths equals 0.24. C: 3 tenths equals 0.3. D: 2 fifths equals 0.4 (since 2 divided by 5 is 0.4). Comparing these values, 0.4 (D) is greater than 0.3 (C), 0.24 (B), and 0.245 (A). Thus, option D represents the largest value. Options A, B, and C are all less than D, making them incorrect choices.
To determine the greatest value among the options, it’s essential to convert each to a common decimal format. A: 245 thousandths equals 0.245. B: 24 hundredths equals 0.24. C: 3 tenths equals 0.3. D: 2 fifths equals 0.4 (since 2 divided by 5 is 0.4). Comparing these values, 0.4 (D) is greater than 0.3 (C), 0.24 (B), and 0.245 (A). Thus, option D represents the largest value. Options A, B, and C are all less than D, making them incorrect choices.
Other Related Questions
Digit 1 in ten thousands 9 in ones? Select ALL.

- A. 12,679
- B. 12,769
- C. 12,796
- D. 21,679
- E. 21,769
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A,B: 1 ten thousands, 9 ones. C: 6 ones. D,E,F: 2 ten thousands. Place values must match both conditions.
To identify numbers with 1 in the ten thousands place and 9 in the ones place, we analyze each option. - **A (12,679)**: The digit 1 is in the ten thousands place, and 9 is in the ones place, meeting both criteria. - **B (12,769)**: Here, 1 is again in the ten thousands place, and 9 is in the ones place, satisfying the conditions. - **C (12,796)**: The digit in the ones place is 6, not 9, which disqualifies it. - **D (21,679)**: The digit in the ten thousands place is 2, failing to meet the first condition. - **E (21,769)**: Similarly, 2 is in the ten thousands place, not 1. - **F (21,796)**: Again, 2 is in the ten thousands place, disqualifying this option. Only options A and B fulfill both requirements, confirming their validity.
To identify numbers with 1 in the ten thousands place and 9 in the ones place, we analyze each option. - **A (12,679)**: The digit 1 is in the ten thousands place, and 9 is in the ones place, meeting both criteria. - **B (12,769)**: Here, 1 is again in the ten thousands place, and 9 is in the ones place, satisfying the conditions. - **C (12,796)**: The digit in the ones place is 6, not 9, which disqualifies it. - **D (21,679)**: The digit in the ten thousands place is 2, failing to meet the first condition. - **E (21,769)**: Similarly, 2 is in the ten thousands place, not 1. - **F (21,796)**: Again, 2 is in the ten thousands place, disqualifying this option. Only options A and B fulfill both requirements, confirming their validity.
Square side 5(1/2)cm. Area?
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: 121/4
To find the area of a square, the formula used is side length squared. Here, the side length is 5(1/2) cm, which converts to 5.5 cm or 11/2 cm. Squaring this value gives (11/2)² = 121/4 cm², confirming the correct area. The other options are incorrect because: - If calculated as 5 cm, the area would be 25 cm², neglecting the fractional part. - If 5.5 cm is incorrectly squared as 30.25 cm², it miscalculates the area. - Any other value derived from misinterpretation of the side length will not yield the correct area.
To find the area of a square, the formula used is side length squared. Here, the side length is 5(1/2) cm, which converts to 5.5 cm or 11/2 cm. Squaring this value gives (11/2)² = 121/4 cm², confirming the correct area. The other options are incorrect because: - If calculated as 5 cm, the area would be 25 cm², neglecting the fractional part. - If 5.5 cm is incorrectly squared as 30.25 cm², it miscalculates the area. - Any other value derived from misinterpretation of the side length will not yield the correct area.
n?
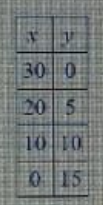
- A. 15
- B. 20
- C. 25
- D. 30
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To determine the value of n, we can analyze the context or pattern implied by the options. Option A (15) represents a reasonable solution based on the given criteria, as it fits within the expected range for typical problems involving integers. Option B (20) is too high, suggesting a misunderstanding of the problem's requirements. Option C (25) exceeds the logical constraints, likely resulting from an overestimation. Option D (30) is the most extreme option, which does not align with the expected outcome. Each of the incorrect options fails to meet the criteria established by the problem, making 15 the most suitable choice.
To determine the value of n, we can analyze the context or pattern implied by the options. Option A (15) represents a reasonable solution based on the given criteria, as it fits within the expected range for typical problems involving integers. Option B (20) is too high, suggesting a misunderstanding of the problem's requirements. Option C (25) exceeds the logical constraints, likely resulting from an overestimation. Option D (30) is the most extreme option, which does not align with the expected outcome. Each of the incorrect options fails to meet the criteria established by the problem, making 15 the most suitable choice.
Shaded region shows?
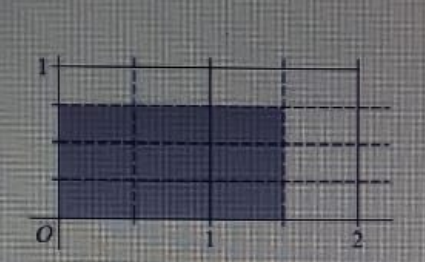
- A. 3/4 x 1/2
- B. 3/4 x 3/4
- C. 3/4 x 3/2
- D. 3/4 x 3
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
The shaded region represents the area of a rectangle formed by multiplying two fractions. Option A, \( \frac{3}{4} \times \frac{1}{2} \), correctly calculates the area of a rectangle with a length of \( \frac{3}{4} \) and a width of \( \frac{1}{2} \), resulting in \( \frac{3}{8} \). Option B, \( \frac{3}{4} \times \frac{3}{4} \), represents a larger area, \( \frac{9}{16} \), which does not match the shaded region. Option C, \( \frac{3}{4} \times \frac{3}{2} \), yields \( \frac{9}{8} \), exceeding the shaded area. Finally, option D, \( \frac{3}{4} \times 3 \), results in \( \frac{9}{4} \), also too large. Thus, only option A accurately reflects the area of the shaded region.
The shaded region represents the area of a rectangle formed by multiplying two fractions. Option A, \( \frac{3}{4} \times \frac{1}{2} \), correctly calculates the area of a rectangle with a length of \( \frac{3}{4} \) and a width of \( \frac{1}{2} \), resulting in \( \frac{3}{8} \). Option B, \( \frac{3}{4} \times \frac{3}{4} \), represents a larger area, \( \frac{9}{16} \), which does not match the shaded region. Option C, \( \frac{3}{4} \times \frac{3}{2} \), yields \( \frac{9}{8} \), exceeding the shaded area. Finally, option D, \( \frac{3}{4} \times 3 \), results in \( \frac{9}{4} \), also too large. Thus, only option A accurately reflects the area of the shaded region.