This passage discusses the first national government in the United States.
In 1781, the 13 former British American colonies established a common government when they ratified the Articles of Confederation. The document established a "firm league of friendship" between the states and reserved the greatest share of political authority to the individual states. The new confederation had only one branch, which was made up of a one-house legislature in which the states were equally represented. Among other powers, the new government had the power to conduct foreign affairs for the 13 independent states. It had the power to make war and peace and to negotiate treaties with foreign countries. It could also settle disputes between the states, Including disputes over western territories. Each of the states retained their "sovereignty, freedom and independence." Under the Articles, Congress could not collect taxes, regulate trade between states, or enforce laws. The confederation was replaced in 1787 by the government created by the U.S. Constitution.
What is the meaning of confederation in this passage?
- A. a government in which the whole population of a country votes to make laws for the people
- B. a political union in which power is divided between a strong central authority and the various other political units
- C. a political union in which the component units retain significant independence from the central government
- D. a government in which people vote to elect representatives who make laws for the people
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
Confederation refers to a political union where individual components maintain considerable autonomy while cooperating for mutual benefit. Option C accurately captures this definition, emphasizing the independence of component units from the central authority. Option A describes a direct democracy, which is not aligned with the concept of confederation. Option B suggests a balance of power that leans towards a strong central authority, contradicting the essence of a confederation. Option D outlines a representative democracy, which does not inherently involve the independence of component units, thus misrepresenting the nature of a confederation.
Confederation refers to a political union where individual components maintain considerable autonomy while cooperating for mutual benefit. Option C accurately captures this definition, emphasizing the independence of component units from the central authority. Option A describes a direct democracy, which is not aligned with the concept of confederation. Option B suggests a balance of power that leans towards a strong central authority, contradicting the essence of a confederation. Option D outlines a representative democracy, which does not inherently involve the independence of component units, thus misrepresenting the nature of a confederation.
Other Related Questions
Which statement is correct about the change in racial and ethnic populations between 2000 and 2010?
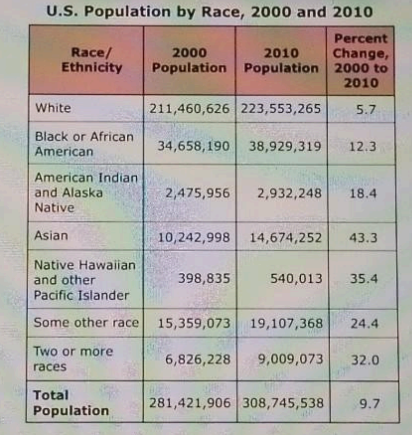
- A. The Black or African American population had the greatest percentage of growth.
- B. The Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander population grew by a greater proportion than the Asian population.
- C. The White population experienced the slowest growth of all groups.
- D. The American Indian and Alaska Native population experienced almost no change.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: B
Option B accurately reflects demographic trends, as the Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander population indeed saw a higher percentage increase compared to the Asian population during this period. Option A is incorrect; while the Black or African American population grew, it was not the greatest percentage increase among all racial groups. Option C misrepresents the data; although the White population's growth was slower compared to previous decades, it was not the slowest overall. Option D is misleading as well; the American Indian and Alaska Native population did experience some growth, albeit modest, rather than remaining unchanged.
Option B accurately reflects demographic trends, as the Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander population indeed saw a higher percentage increase compared to the Asian population during this period. Option A is incorrect; while the Black or African American population grew, it was not the greatest percentage increase among all racial groups. Option C misrepresents the data; although the White population's growth was slower compared to previous decades, it was not the slowest overall. Option D is misleading as well; the American Indian and Alaska Native population did experience some growth, albeit modest, rather than remaining unchanged.
This flow chart traces development of democratic government in England. Which event completes this sequence?

- A. The English Bill of Rights gave the king power to appoint most members of Parliament.
- B. The Magna Carta forced the nobles to give up their feudal lands.
- C. The English Bill of Rights guaranteed suffrage to most male citizens.
- D. The Magna Carta forced the king to share his political power.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
The correct choice, D, highlights the Magna Carta's pivotal role in limiting the king's absolute power and initiating the concept of shared governance. This foundational document established that the monarch must consult nobles before making decisions, laying the groundwork for parliamentary democracy. Option A is incorrect as the English Bill of Rights actually limited the king's power over Parliament, not enhanced it. Option B misrepresents the Magna Carta's purpose; it did not force nobles to relinquish their lands, but rather addressed their grievances against the king. Option C is also inaccurate, as the English Bill of Rights did not guarantee suffrage but focused on limiting royal authority and protecting certain rights.
The correct choice, D, highlights the Magna Carta's pivotal role in limiting the king's absolute power and initiating the concept of shared governance. This foundational document established that the monarch must consult nobles before making decisions, laying the groundwork for parliamentary democracy. Option A is incorrect as the English Bill of Rights actually limited the king's power over Parliament, not enhanced it. Option B misrepresents the Magna Carta's purpose; it did not force nobles to relinquish their lands, but rather addressed their grievances against the king. Option C is also inaccurate, as the English Bill of Rights did not guarantee suffrage but focused on limiting royal authority and protecting certain rights.
Which event occurred first?
- A. Michael moved to Ohio.
- B. Michael attained U.S. citizenship.
- C. The IRO was created.
- D. The UN was established.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To determine the sequence of events, it’s essential to consider historical timelines. The United Nations (UN) was established in 1945, laying the groundwork for international cooperation. The International Refugee Organization (IRO) was created shortly after, in 1946, to address post-war refugee issues. Michael attaining U.S. citizenship likely occurred after these events, as it typically follows immigration processes. Lastly, Michael moving to Ohio would depend on his citizenship status and individual circumstances, making it the most recent event in this context.
To determine the sequence of events, it’s essential to consider historical timelines. The United Nations (UN) was established in 1945, laying the groundwork for international cooperation. The International Refugee Organization (IRO) was created shortly after, in 1946, to address post-war refugee issues. Michael attaining U.S. citizenship likely occurred after these events, as it typically follows immigration processes. Lastly, Michael moving to Ohio would depend on his citizenship status and individual circumstances, making it the most recent event in this context.
Which statement about the ratification of the 19th Amendment is based on the passage?
- A. Ratification was the result of the Seneca Falls Convention.
- B. Ratification occurred in return for the military service of women during World War I.
- C. Ratification occurred prior to the granting of voting rights to freed slaves.
- D. Ratification was the result of the accumulated efforts of women for decades.
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
The ratification of the 19th Amendment was the culmination of decades of advocacy and activism by women who fought tirelessly for their voting rights, making option D the most accurate statement. Option A incorrectly attributes the ratification solely to the Seneca Falls Convention, which was just one of many events in the long struggle for women's suffrage. Option B suggests a direct exchange of military service for voting rights, which oversimplifies the complex social and political factors involved. Option C misrepresents the timeline, as the 19th Amendment was ratified after the Civil War, but the fight for voting rights for freed slaves and women evolved concurrently, not sequentially.
The ratification of the 19th Amendment was the culmination of decades of advocacy and activism by women who fought tirelessly for their voting rights, making option D the most accurate statement. Option A incorrectly attributes the ratification solely to the Seneca Falls Convention, which was just one of many events in the long struggle for women's suffrage. Option B suggests a direct exchange of military service for voting rights, which oversimplifies the complex social and political factors involved. Option C misrepresents the timeline, as the 19th Amendment was ratified after the Civil War, but the fight for voting rights for freed slaves and women evolved concurrently, not sequentially.