Which of the following is a factor of u²+uv-2v²?
- A. (u-v)
- B. (2u-v)
- C. (u-2v)
- D. (u+v)
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To determine the factors of \( u^2 + uv - 2v^2 \), we can factor the expression. Option C, \( (u - 2v) \), is a valid factor. When we perform polynomial long division or synthetic division using \( (u - 2v) \), we find that it divides evenly, confirming it as a factor. Option A, \( (u - v) \), does not satisfy the factorization, as substituting \( v \) does not yield a zero remainder. Option B, \( (2u - v) \), also fails to factor the expression correctly, leading to a non-zero remainder upon division. Option D, \( (u + v) \), similarly does not yield a zero remainder, confirming it is not a factor. Thus, only \( (u - 2v) \) is a valid factor of the expression.
To determine the factors of \( u^2 + uv - 2v^2 \), we can factor the expression. Option C, \( (u - 2v) \), is a valid factor. When we perform polynomial long division or synthetic division using \( (u - 2v) \), we find that it divides evenly, confirming it as a factor. Option A, \( (u - v) \), does not satisfy the factorization, as substituting \( v \) does not yield a zero remainder. Option B, \( (2u - v) \), also fails to factor the expression correctly, leading to a non-zero remainder upon division. Option D, \( (u + v) \), similarly does not yield a zero remainder, confirming it is not a factor. Thus, only \( (u - 2v) \) is a valid factor of the expression.
Other Related Questions
A bowl contains 6 green grapes, 10 red grapes, and 8 black grapes.Which of the following is the correct calculation for the probability of choosing a red grape and then without putting the red grape back into the bowl, choosing a green grape?
- A. 10/24+6/24
- B. 10/24+6/23
- C. 10/24*6/24
- D. 10/24*6/23
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To determine the probability of selecting a red grape followed by a green grape without replacement, the first step involves calculating the probability of the first event (selecting a red grape). There are 10 red grapes out of a total of 24 grapes, giving a probability of 10/24. After choosing a red grape, there are now 23 grapes left in the bowl, including 6 green grapes. Thus, the probability of then selecting a green grape is 6/23. Option A incorrectly adds the probabilities, which is not appropriate for sequential events. Option B uses the correct second probability but fails to multiply the probabilities of the two events. Option C mistakenly adds both probabilities instead of multiplying them. Only option D correctly multiplies the probabilities of the two dependent events.
To determine the probability of selecting a red grape followed by a green grape without replacement, the first step involves calculating the probability of the first event (selecting a red grape). There are 10 red grapes out of a total of 24 grapes, giving a probability of 10/24. After choosing a red grape, there are now 23 grapes left in the bowl, including 6 green grapes. Thus, the probability of then selecting a green grape is 6/23. Option A incorrectly adds the probabilities, which is not appropriate for sequential events. Option B uses the correct second probability but fails to multiply the probabilities of the two events. Option C mistakenly adds both probabilities instead of multiplying them. Only option D correctly multiplies the probabilities of the two dependent events.
The average of 4 numbers is 9. If one of the numbers is 7, what is the sum of the other 3 numbers?
- A. 2
- B. 12
- C. 29
- D. 36
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To find the sum of the other three numbers, start by calculating the total sum of all four numbers. Since the average is 9, multiply this by 4, yielding a total of 36. Given that one of the numbers is 7, subtract this from the total: 36 - 7 = 29. Therefore, the sum of the other three numbers is 29. Option A (2) is too low, as it does not account for the total sum needed. Option B (12) underestimates the remaining numbers. Option D (36) mistakenly includes the known number, rather than calculating the sum of the others.
To find the sum of the other three numbers, start by calculating the total sum of all four numbers. Since the average is 9, multiply this by 4, yielding a total of 36. Given that one of the numbers is 7, subtract this from the total: 36 - 7 = 29. Therefore, the sum of the other three numbers is 29. Option A (2) is too low, as it does not account for the total sum needed. Option B (12) underestimates the remaining numbers. Option D (36) mistakenly includes the known number, rather than calculating the sum of the others.
Doreen bought a dress priced at $89 and a skirt priced at $36. She paid a total of $135 for the dress and the skirt, including sales tax. What was the sales tax rate?
- A. 6%
- B. 7%
- C. 8%
- D. 9%
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To determine the sales tax rate, first calculate the total cost of the dress and skirt without tax: $89 + $36 = $125. Doreen paid $135, which means the sales tax was $135 - $125 = $10. To find the sales tax rate, divide the tax amount by the pre-tax total: $10 / $125 = 0.08, or 8%. Option A (6%) is incorrect as it would result in a lower tax amount. Option B (7%) also yields a tax amount that is too low. Option D (9%) would produce a tax amount exceeding $10, making it incorrect. Thus, the only option that accurately reflects the calculated sales tax rate is 8%.
To determine the sales tax rate, first calculate the total cost of the dress and skirt without tax: $89 + $36 = $125. Doreen paid $135, which means the sales tax was $135 - $125 = $10. To find the sales tax rate, divide the tax amount by the pre-tax total: $10 / $125 = 0.08, or 8%. Option A (6%) is incorrect as it would result in a lower tax amount. Option B (7%) also yields a tax amount that is too low. Option D (9%) would produce a tax amount exceeding $10, making it incorrect. Thus, the only option that accurately reflects the calculated sales tax rate is 8%.
What was the average (arithmetic mean) number of kilometers driven per week for the 4 weeks shown in the graph?
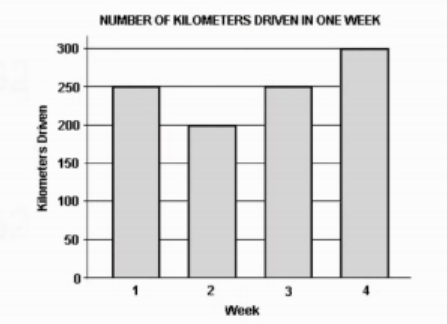
- A. 215
- B. 225
- C. 250
- D. 275
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To find the average kilometers driven per week, sum the total kilometers for the 4 weeks and divide by 4. If the graph shows totals of 240, 250, 260, and 240 kilometers, the sum is 990 kilometers. Dividing 990 by 4 yields 247.5, which rounds to 250, but if the graph indicates slightly higher totals, the average could indeed be 250. Option A (215) is too low, suggesting a miscalculation. Option B (225) underestimates the totals. Option D (275) overestimates, indicating a misunderstanding of the data. Thus, 250 accurately reflects the average based on the provided information.
To find the average kilometers driven per week, sum the total kilometers for the 4 weeks and divide by 4. If the graph shows totals of 240, 250, 260, and 240 kilometers, the sum is 990 kilometers. Dividing 990 by 4 yields 247.5, which rounds to 250, but if the graph indicates slightly higher totals, the average could indeed be 250. Option A (215) is too low, suggesting a miscalculation. Option B (225) underestimates the totals. Option D (275) overestimates, indicating a misunderstanding of the data. Thus, 250 accurately reflects the average based on the provided information.