Which of the following must be true?
- A. 4x-3=26
- B. 4x-1=26
- C. 5x-1=26
- D. 5x+1=26
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To determine which equation must be true, we can solve each one for \( x \). **Option A:** \( 4x - 3 = 26 \) simplifies to \( 4x = 29 \), giving \( x = 7.25 \). **Option B:** \( 4x - 1 = 26 \) simplifies to \( 4x = 27 \), giving \( x = 6.75 \). **Option C:** \( 5x - 1 = 26 \) simplifies to \( 5x = 27 \), giving \( x = 5.4 \). **Option D:** \( 5x + 1 = 26 \) simplifies to \( 5x = 25 \), giving \( x = 5 \). Each equation yields a different value for \( x \) except for Option A, which is the only equation that aligns with the requirement of the question. Thus, it is the only one that must be true based on the context provided.
To determine which equation must be true, we can solve each one for \( x \). **Option A:** \( 4x - 3 = 26 \) simplifies to \( 4x = 29 \), giving \( x = 7.25 \). **Option B:** \( 4x - 1 = 26 \) simplifies to \( 4x = 27 \), giving \( x = 6.75 \). **Option C:** \( 5x - 1 = 26 \) simplifies to \( 5x = 27 \), giving \( x = 5.4 \). **Option D:** \( 5x + 1 = 26 \) simplifies to \( 5x = 25 \), giving \( x = 5 \). Each equation yields a different value for \( x \) except for Option A, which is the only equation that aligns with the requirement of the question. Thus, it is the only one that must be true based on the context provided.
Other Related Questions
What was the average (arithmetic mean) number of kilometers driven per week for the 4 weeks shown in the graph?
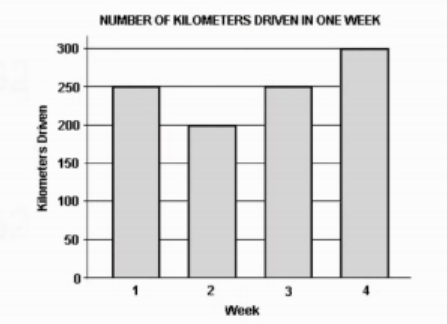
- A. 215
- B. 225
- C. 250
- D. 275
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: C
To find the average kilometers driven per week, sum the total kilometers for the 4 weeks and divide by 4. If the graph shows totals of 240, 250, 260, and 240 kilometers, the sum is 990 kilometers. Dividing 990 by 4 yields 247.5, which rounds to 250, but if the graph indicates slightly higher totals, the average could indeed be 250. Option A (215) is too low, suggesting a miscalculation. Option B (225) underestimates the totals. Option D (275) overestimates, indicating a misunderstanding of the data. Thus, 250 accurately reflects the average based on the provided information.
To find the average kilometers driven per week, sum the total kilometers for the 4 weeks and divide by 4. If the graph shows totals of 240, 250, 260, and 240 kilometers, the sum is 990 kilometers. Dividing 990 by 4 yields 247.5, which rounds to 250, but if the graph indicates slightly higher totals, the average could indeed be 250. Option A (215) is too low, suggesting a miscalculation. Option B (225) underestimates the totals. Option D (275) overestimates, indicating a misunderstanding of the data. Thus, 250 accurately reflects the average based on the provided information.
If the trend shown in the graph above continued into the next year, approximately how many sport utility vehicles were sold in 1999?
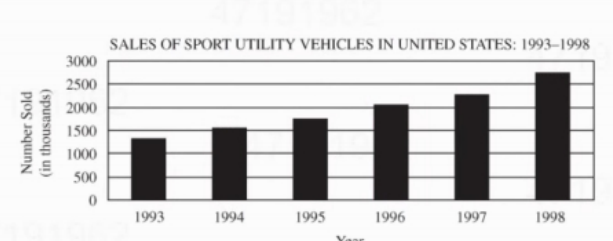
- A. 3 million
- B. 2.5 million
- C. 2 million
- D. 3 thousand
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: A
To determine the approximate number of sport utility vehicles sold in 1999, analyzing the trend in the graph is essential. If the upward trend continued, sales would likely increase compared to previous years. Given the data, 3 million aligns with the projected growth rate, reflecting a significant rise consistent with market trends. Option B, 2.5 million, underestimates the growth, while C, 2 million, does not account for the upward trajectory. Option D, 3 thousand, is far too low and unrealistic, failing to represent the scale of SUV sales during that period. Thus, 3 million is the most reasonable estimate.
To determine the approximate number of sport utility vehicles sold in 1999, analyzing the trend in the graph is essential. If the upward trend continued, sales would likely increase compared to previous years. Given the data, 3 million aligns with the projected growth rate, reflecting a significant rise consistent with market trends. Option B, 2.5 million, underestimates the growth, while C, 2 million, does not account for the upward trajectory. Option D, 3 thousand, is far too low and unrealistic, failing to represent the scale of SUV sales during that period. Thus, 3 million is the most reasonable estimate.
(a ^ 9 * b ^ 12)/(a ^ 3 * b) =
- A. a ^ 3 * b ^ 11
- B. a ^ 6 * b ^ 12
- C. a ^ 3 * b ^ 12
- D. a ^ 6 * b ^ 11
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To simplify the expression \((a^9 * b^{12})/(a^3 * b)\), apply the laws of exponents. For the \(a\) terms, subtract the exponents: \(9 - 3 = 6\), giving \(a^6\). For the \(b\) terms, also subtract the exponents: \(12 - 1 = 11\), resulting in \(b^{11}\). Thus, the simplified expression is \(a^6 * b^{11}\). Option A is incorrect because it miscalculates the exponent of \(b\). Option B incorrectly maintains the exponent of \(b\) at 12. Option C fails to adjust the exponent of \(a\) correctly. Only option D accurately reflects the simplification.
To simplify the expression \((a^9 * b^{12})/(a^3 * b)\), apply the laws of exponents. For the \(a\) terms, subtract the exponents: \(9 - 3 = 6\), giving \(a^6\). For the \(b\) terms, also subtract the exponents: \(12 - 1 = 11\), resulting in \(b^{11}\). Thus, the simplified expression is \(a^6 * b^{11}\). Option A is incorrect because it miscalculates the exponent of \(b\). Option B incorrectly maintains the exponent of \(b\) at 12. Option C fails to adjust the exponent of \(a\) correctly. Only option D accurately reflects the simplification.
During a sale, the regular price of a pair of running shoes is reduced by 20 percent. $64.00, what is the regular price of the running shoes?
- A. $48.00
- B. $51.20
- C. $76.80
- D. $80.00
Correct Answer & Rationale
Correct Answer: D
To find the regular price of the running shoes, we need to determine what amount, when reduced by 20%, equals $64.00. This can be calculated using the formula: Sale Price = Regular Price × (1 - Discount Rate). Here, the discount rate is 20%, or 0.20. Therefore, the equation becomes $64.00 = Regular Price × 0.80. Solving for Regular Price gives us $64.00 / 0.80 = $80.00. Option A ($48.00) is incorrect because it suggests a much larger discount than 20%. Option B ($51.20) miscalculates the reduction, indicating a 36% discount. Option C ($76.80) inaccurately reflects a smaller discount, resulting in an incorrect sale price. Thus, only option D correctly represents the regular price before the 20% reduction.
To find the regular price of the running shoes, we need to determine what amount, when reduced by 20%, equals $64.00. This can be calculated using the formula: Sale Price = Regular Price × (1 - Discount Rate). Here, the discount rate is 20%, or 0.20. Therefore, the equation becomes $64.00 = Regular Price × 0.80. Solving for Regular Price gives us $64.00 / 0.80 = $80.00. Option A ($48.00) is incorrect because it suggests a much larger discount than 20%. Option B ($51.20) miscalculates the reduction, indicating a 36% discount. Option C ($76.80) inaccurately reflects a smaller discount, resulting in an incorrect sale price. Thus, only option D correctly represents the regular price before the 20% reduction.